Key Points/Overview
When the normal drinking water supply is interrupted or contaminated, chlorine bleach can safely disinfect non-potable water. Chlorine bleach also helps keep swimming pools free of waterborne germs that can cause issues such as diarrhea and swimmer’s ear.
Diluted chlorine bleach solutions can be used to help disinfect household surfaces in bathrooms and the kitchen. Using bleach solutions to disinfect frequently touched surfaces can help prevent the spread of colds, flu, norovirus and other infectious illnesses.
Chlorine bleach solutions help disinfect reusable equipment in hospitals, medical labs, doctors’ offices, and nursing homes to help prevent the spread of infectious illnesses among patients, residents and healthcare professionals.
While chlorine bleach is generally safe to use in a variety of everyday household applications, users should follow the manufacturer’s directions on the product label. Chlorine bleach should not be used at full strength.
Uses & Benefits
Chlorine bleach is primarily known as a laundry cleaning and disinfecting product that destroys germs and helps make white clothes whiter. Bleach also has a wide range of other applications, including:

Safe water
Before chlorine-based disinfectants like sodium hypochlorite solutions were routinely added to U.S. drinking water beginning over 100 years ago, many people became sick and died of waterborne diseases, such as cholera and typhoid fever. Chlorination destroys most waterborne germs to help keep drinking water safe. During emergencies, when the normal drinking water supply is interrupted or contaminated, chlorine bleach can safely disinfect non-potable water. Chlorine bleach also helps keep swimming pools free of waterborne germs that can cause diarrhea, swimmer’s ear and “hot tub rash.”

Safe food production and preparation
Chlorine bleach added to water can destroy germs associated with raw foods. These solutions also can disinfect food production equipment, food preparation surfaces and food-transportation containers. Grocery stores and restaurants use bleach solutions to help sanitize food storage and preparation surfaces.
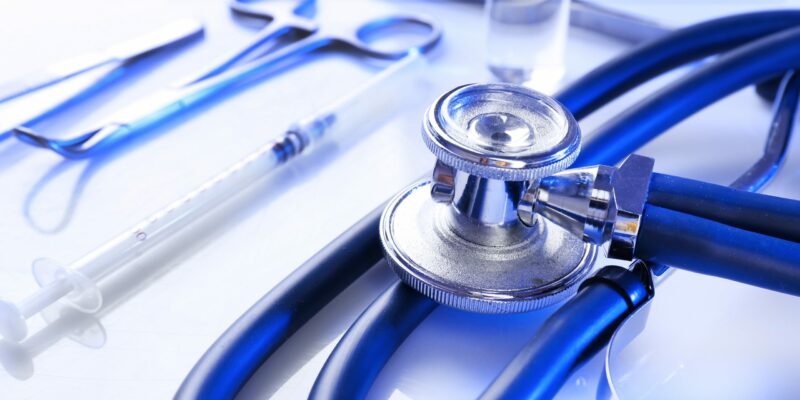
Medical uses
Chlorine bleach solutions help disinfect many types of surfaces, including reusable equipment in hospitals, medical labs, doctors’ offices, and nursing homes, to help prevent the spread of infectious illnesses among patients, residents and healthcare professionals.

Household disinfection
Consumers can use diluted chlorine bleach solutions to help disinfect household surfaces in bathrooms and the kitchen. Using bleach solutions to disinfect frequently touched surfaces also can help prevent the spread of colds, flu, norovirus and other infectious illnesses. During natural disasters, such as flooding, chlorine bleach can disinfect contaminated surfaces.

Safety Information
Chlorine bleach that is registered with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency1 is safe to use in everyday household applications, but users should take care to follow manufacturer’s directions on the product label. Chlorine bleach should never be used full strength; for specific applications, users should dilute the product with water according to label directions.
Chlorine bleach is corrosive, so users should avoid contact with the eyes and skin by wearing protective eyewear and plastic or rubber gloves and ensure good air ventilation when using bleach in a confined area.
It is important to store chlorine bleach out of the reach of children. Additionally, storing bleach out of direct sunlight and away from sources of heat can help extend its shelf life, as heat and light degrade this product over time.
Consumers should never mix chlorine bleach or any product containing chlorine bleach with ammonia,2 ammonia-based products or acidic products, as the combination can produce a toxic vapor.3


