Key Points/Overview
Silicones provide essential benefits in key segments of our economy, including health care, aerospace, personal care, electronics, transportation, and construction.
Silicones can enhance products by providing more flexibility and resistance to moisture, heat, cold, and ultraviolet radiation.
The human health and environmental impacts of silicone products are extensively studied by the global silicone industry and independent scientists. Several studies and regulatory assessments support the safe use of silicone materials in many applications.
Uses & Benefits
Silicones impart a number of benefits to the products in which they are used, including enhanced flexibility and moisture, heat, cold and ultraviolet radiation resistance. Silicones can be manufactured in many forms, including solids, liquids, semi-viscous pastes, greases, oils and rubber.

Personal Care Products
Silicones used in personal care products reduce the white residue and tacky feel of antiperspirants in deodorants. They are also “long-lasting” and help to retain the color and luster associated with cosmetics, shampoos and conditioners, as well as impart better shine, and allow skin care products to be made with stronger SPF. Wetting and spreading qualities provide for smooth and even application of cosmetics, lotions, sunscreens and cleansers.

Energy
Silicone improves the efficiency, durability and performance of solar panels and photovoltaic devices, making them more cost-effective. Because they can withstand the sun for years, silicones are ideal materials for solar panel and photovoltaic applications.
Electronics
Keypads, keyboards and copier rollers are made with sturdy, durable silicones – as are many components of computers, mobile electronics and home entertainment equipment. Silicones also play an essential role in enabling LED lighting technology. Silicones high thermal stability and excellent dielectric properties allow for use in a variety of electrical transmission applications.

Aviation
Because silicones can withstand stress and temperature extremes, silicone adhesives and sealants are used to seal and protect doors, windows, wings, fuel tanks, hydraulic switches, overhead bins, wing edges, landing gear electrical devices, vent ducts, engine gaskets, electrical wires and black boxes.
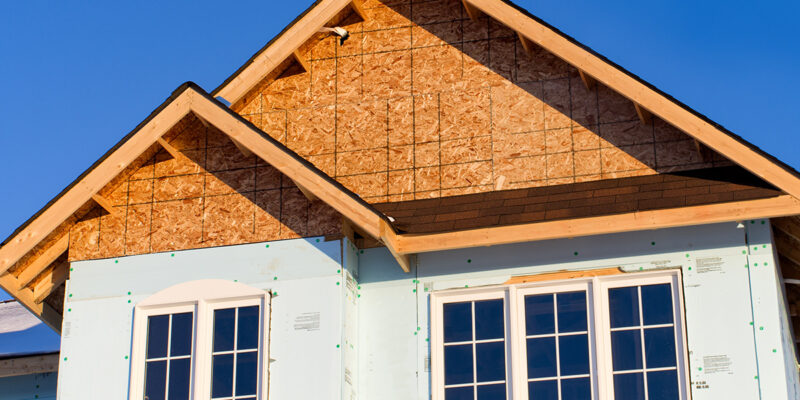

Construction and Architecture
Silicones are key to construction and renovation of commercial and residential buildings – from enabling glass walled skyscrapers to enabling energy efficient architecture. At home, silicone sealants and caulks are used to reduce energy usage and prevent damage from moisture and bacteria build-up.
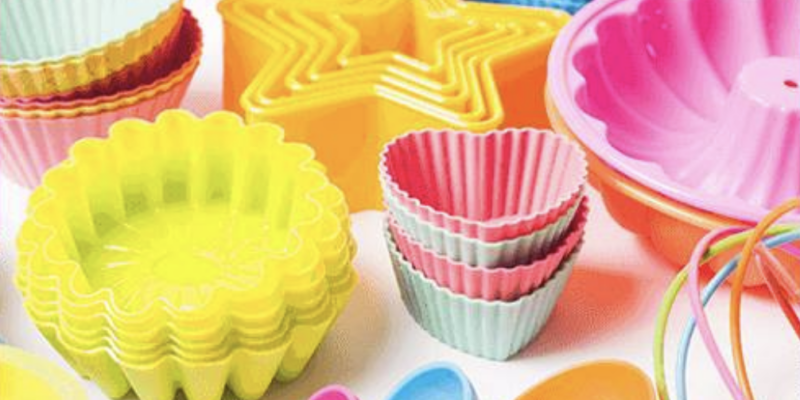

Kitchenware
The flexible, non-stick surface of silicone bakeware and cookware is easy to clean and does not impart flavor or odor to food. Cake pans, muffin molds, and baking mats can go from the freezer to the oven, microwave or dishwasher without affecting food taste or quality.
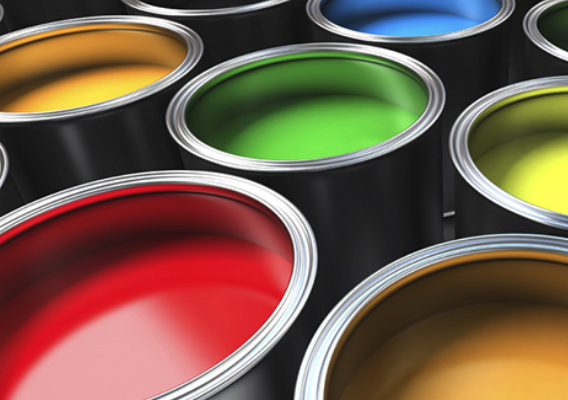

Paints and Coatings
Newer silicone-enhanced paints keep the exterior coatings of houses, bridges and railway cars flexible so they withstand freeze and thaw cycles without cracking. Silicone coatings on highway, oil rig and road surfaces are less likely to corrode due to exposure to oils, gasoline, salt spray and acid rain.

Sporting Goods and Apparel
Silicones seal out water from goggles and diving masks. Silicones enable new techniques to design sportswear that is lightweight, durable, water repellent and high performing, while allowing the fabric to maintain “breathability.”

Safety Information
The global silicone industry and independent scientists extensively study the human health and environmental impacts of silicone products. The following studies and regulatory assessments support the safe use of silicone materials in a wide variety of applications:
- Regulatory agencies in Canada have extensively reviewed significant amounts of scientific data and have concluded those silicone materials satisfy regulatory requirements for human health and the environment.
- Federal government agency Health Canada assessed silicones commonly used in consumer products and concluded that they “[are] not entering the environment in a quantity or concentration or under conditions that constitute or may constitute a danger in Canada to human life or health.”
- Taking into account all of the available scientific information, the Report of the Canadian Board of Review concluded that the “Siloxane D5 does not pose a danger to the environment. There is no evidence to demonstrate that Siloxane D5 is toxic to any organism.” The Board also states that Siloxane D5 “will not accumulate to sufficiently great concentrations to cause adverse effects in organisms in air, water, soils or sediments.”
- EU’s Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS) is of the opinion that silicones do not pose a risk for human health when used in cosmetic products.
- An expert scientific panel – Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) – has concluded that silicones do not pose a risk to human health from their use in cosmetics.
Tested, Effective, Affordable
Silicone manufacturers voluntarily support health and environmental testing to provide greater scientific understanding of silicone materials used in consumer and industrial applications. The goal of the research is to communicate relevant research and safety information to regulatory agencies, employees and customers.
Silicones’ versatility stems from their performance and protective qualities. Silicones are used across some of the most strenuous and yet some of the most sensitive applications. They add “industrial” to the “strength” of coatings, sealants and joints in skyscrapers, bridges, highways and ocean vessels. Used in personal care products and health care, they make lotions, topical medications and skin adhesives easy to apply and less irritating.


